Overview

Flat feet, fallen arches, or ?pes planus? is normally a symptomless and fortunately painless condition. It is characterized by the arch of the foot collapsing completely, which causes the entire sole of the foot to come into perfect contact with the ground. An estimated 20-30 percent of the entire population has some form of flat feet, ranging in severity from asymptomatic to somewhat problematic. Most people who endure this problem are able to experience life pain and symptom free from the nearly unnoticeable abnormality. However, a small sector of those affected do experience pain or discomfort, which is when a treatment program needs to be put in action.
Causes
A fallen arch occurs because one of the main structures that support the arch has broken or torn. Usually it occurs without trauma, although a small injury associated with the onset of the pain is often recalled, it is sometimes difficult to determine whether the injury was clearly big enough to permanently injure the leg. I suspect that even before the symptoms that the structure that broke was weakening and the injury was simply the ?needle that broke the camels back?. The structure that is most commonly torn is the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon is attached to a muscle on the inside of the back of the ankle, and runs along the medial malleolus, the bony prominence on the inside of the ankle, to attach to a bone in the arch called the navicular bone. It usually begins to weaken and stretch along the back of the medial malleolus. It often begins as a swelling and the arch flattens over the next several weeks to months. As the arch flattens, other structures that support the arch begin to stretch and tear. The bones along the outside of the ankle begin to crush together, causing pain and swelling in this are, and the toes may tilt to the outside as the arch collapses. It is not known why this process begins. It is often associated with diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. It also is more common as a person enters the fifty to seventy year age range. ?Fallen arches? are much more common in people who are already flat footed.
Symptoms
Fallen arches may induce pain in the heel, the inside of the arch, the ankle, and may even extend up the body into the leg (shin splints), knee, lower back and hip. You may also experience inflammation (swelling, redness, heat and pain) along the inside of the ankle (along the posterior tibial tendon). Additionally, you may notice some changes in the way your foot looks. Your ankle may begin to turn inward (pronate), causing the bottom of your heel to tilt outward. Other secondary symptoms may also show up as the condition progresses, such as hammertoes or bunions. You may also want to check your footprint after you step out of the shower. (It helps if you pretend you?re in a mystery novel, and you?re leaving wet, footprinty clues that will help crack the case.) Normally, you can see a clear imprint of the front of your foot (the ball and the toes) the heel, and the outside edge of your foot. There should be a gap (i.e. no footprinting) along the inside where your arches are. If your foot is flat, it?ll probably leave an imprint of the full bottom of your foot-no gap to be had. Your shoes may also be affected: because the ankle tilts somewhat with this condition, the heel of your shoes may become more worn on one side than another.
Diagnosis
Many medical professionals can diagnose a flat foot by examining the patient standing or just looking at them. On going up onto tip toe the deformity will correct when this is a flexible flat foot in a child with lax joints. Such correction is not seen in the adult with a rigid flat foot. An easy and traditional home diagnosis is the "wet footprint" test, performed by wetting the feet in water and then standing on a smooth, level surface such as smooth concrete or thin cardboard or heavy paper. Usually, the more the sole of the foot that makes contact (leaves a footprint), the flatter the foot. In more extreme cases, known as a kinked flatfoot, the entire inner edge of the footprint may actually bulge outward, where in a normal to high arch this part of the sole of the foot does not make contact with the ground at all.
bestshoelifts
Non Surgical Treatment
The type of treatment will depend on the stage of PTTD present. There are four stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Stage I. The posterior tibial tendon is inflamed but has normal strength. There is little to no change in the arch of the foot. The patient can still perform a single-limb heel rise and has a flexible hindfoot. Orthotic treatment options include modified off the shelf inserts and custom molded orthotics. Stage 2. The tendon is partially torn or shows degenerative changes and as a result loses strength.There is considerable flattening of the arch without arthritic changes in the foot. The patient cannot perform single-limb heel rise. Pain is now present on the lateral aspect of the ankle. Orthotic treatment is similar as that in stage I, with the addition of more rigid arch supports and wedging. Stage 3. Results when the posterior tibial tendon is torn and not functioning. As a result the arch is completely collapsed with arthritic changes in the foot. A solid ankle AFO is suggested in conjunction with a modified orthopedic shoe. Stage 4. Is identical to stage three except that the ankle joint also becomes arthritic. A rigid AFO and modified orthopedic shoe is required.
Surgical Treatment

A better approach is to strengthen the weakened ligaments with Prolotherapy, supplemented by an arch support if the condition has existed for several years. Chronic pain is most commonly due to tendon and ligament weakness, or cartilage deterioration. The safest and most effective natural medicine treatment for repairing tendon, ligament and cartilage damage is Prolotherapy. In simple terms, Prolotherapy stimulates the body to repair painful areas. It does so by inducing a mild inflammatory reaction in the weakened ligaments and cartilage. Since the body heals by inflammation, Prolotherapy stimulates healing. Prolotherapy offers the most curative results in treating chronic pain. It effectively eliminates pain because it attacks the source: the fibro-osseous junction, an area rich in sensory nerves. What?s more, the tissue strengthening and pain relief stimulated by Prolotherapy is permanent.

Flat feet, fallen arches, or ?pes planus? is normally a symptomless and fortunately painless condition. It is characterized by the arch of the foot collapsing completely, which causes the entire sole of the foot to come into perfect contact with the ground. An estimated 20-30 percent of the entire population has some form of flat feet, ranging in severity from asymptomatic to somewhat problematic. Most people who endure this problem are able to experience life pain and symptom free from the nearly unnoticeable abnormality. However, a small sector of those affected do experience pain or discomfort, which is when a treatment program needs to be put in action.
Causes
A fallen arch occurs because one of the main structures that support the arch has broken or torn. Usually it occurs without trauma, although a small injury associated with the onset of the pain is often recalled, it is sometimes difficult to determine whether the injury was clearly big enough to permanently injure the leg. I suspect that even before the symptoms that the structure that broke was weakening and the injury was simply the ?needle that broke the camels back?. The structure that is most commonly torn is the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon is attached to a muscle on the inside of the back of the ankle, and runs along the medial malleolus, the bony prominence on the inside of the ankle, to attach to a bone in the arch called the navicular bone. It usually begins to weaken and stretch along the back of the medial malleolus. It often begins as a swelling and the arch flattens over the next several weeks to months. As the arch flattens, other structures that support the arch begin to stretch and tear. The bones along the outside of the ankle begin to crush together, causing pain and swelling in this are, and the toes may tilt to the outside as the arch collapses. It is not known why this process begins. It is often associated with diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. It also is more common as a person enters the fifty to seventy year age range. ?Fallen arches? are much more common in people who are already flat footed.
Symptoms
Fallen arches may induce pain in the heel, the inside of the arch, the ankle, and may even extend up the body into the leg (shin splints), knee, lower back and hip. You may also experience inflammation (swelling, redness, heat and pain) along the inside of the ankle (along the posterior tibial tendon). Additionally, you may notice some changes in the way your foot looks. Your ankle may begin to turn inward (pronate), causing the bottom of your heel to tilt outward. Other secondary symptoms may also show up as the condition progresses, such as hammertoes or bunions. You may also want to check your footprint after you step out of the shower. (It helps if you pretend you?re in a mystery novel, and you?re leaving wet, footprinty clues that will help crack the case.) Normally, you can see a clear imprint of the front of your foot (the ball and the toes) the heel, and the outside edge of your foot. There should be a gap (i.e. no footprinting) along the inside where your arches are. If your foot is flat, it?ll probably leave an imprint of the full bottom of your foot-no gap to be had. Your shoes may also be affected: because the ankle tilts somewhat with this condition, the heel of your shoes may become more worn on one side than another.
Diagnosis
Many medical professionals can diagnose a flat foot by examining the patient standing or just looking at them. On going up onto tip toe the deformity will correct when this is a flexible flat foot in a child with lax joints. Such correction is not seen in the adult with a rigid flat foot. An easy and traditional home diagnosis is the "wet footprint" test, performed by wetting the feet in water and then standing on a smooth, level surface such as smooth concrete or thin cardboard or heavy paper. Usually, the more the sole of the foot that makes contact (leaves a footprint), the flatter the foot. In more extreme cases, known as a kinked flatfoot, the entire inner edge of the footprint may actually bulge outward, where in a normal to high arch this part of the sole of the foot does not make contact with the ground at all.
bestshoelifts
Non Surgical Treatment
The type of treatment will depend on the stage of PTTD present. There are four stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Stage I. The posterior tibial tendon is inflamed but has normal strength. There is little to no change in the arch of the foot. The patient can still perform a single-limb heel rise and has a flexible hindfoot. Orthotic treatment options include modified off the shelf inserts and custom molded orthotics. Stage 2. The tendon is partially torn or shows degenerative changes and as a result loses strength.There is considerable flattening of the arch without arthritic changes in the foot. The patient cannot perform single-limb heel rise. Pain is now present on the lateral aspect of the ankle. Orthotic treatment is similar as that in stage I, with the addition of more rigid arch supports and wedging. Stage 3. Results when the posterior tibial tendon is torn and not functioning. As a result the arch is completely collapsed with arthritic changes in the foot. A solid ankle AFO is suggested in conjunction with a modified orthopedic shoe. Stage 4. Is identical to stage three except that the ankle joint also becomes arthritic. A rigid AFO and modified orthopedic shoe is required.
Surgical Treatment

A better approach is to strengthen the weakened ligaments with Prolotherapy, supplemented by an arch support if the condition has existed for several years. Chronic pain is most commonly due to tendon and ligament weakness, or cartilage deterioration. The safest and most effective natural medicine treatment for repairing tendon, ligament and cartilage damage is Prolotherapy. In simple terms, Prolotherapy stimulates the body to repair painful areas. It does so by inducing a mild inflammatory reaction in the weakened ligaments and cartilage. Since the body heals by inflammation, Prolotherapy stimulates healing. Prolotherapy offers the most curative results in treating chronic pain. It effectively eliminates pain because it attacks the source: the fibro-osseous junction, an area rich in sensory nerves. What?s more, the tissue strengthening and pain relief stimulated by Prolotherapy is permanent.





 Morton?s Neuroma is a common foot condition characterized by pain and swelling in the ball of the foot, between the third and fourth toes. It?s caused by bones in your feet squeezing a nerve. Symptoms include a sharp, burning pain and possibly separation between the affected toes.
Morton?s Neuroma is a common foot condition characterized by pain and swelling in the ball of the foot, between the third and fourth toes. It?s caused by bones in your feet squeezing a nerve. Symptoms include a sharp, burning pain and possibly separation between the affected toes.




 Overview
Overview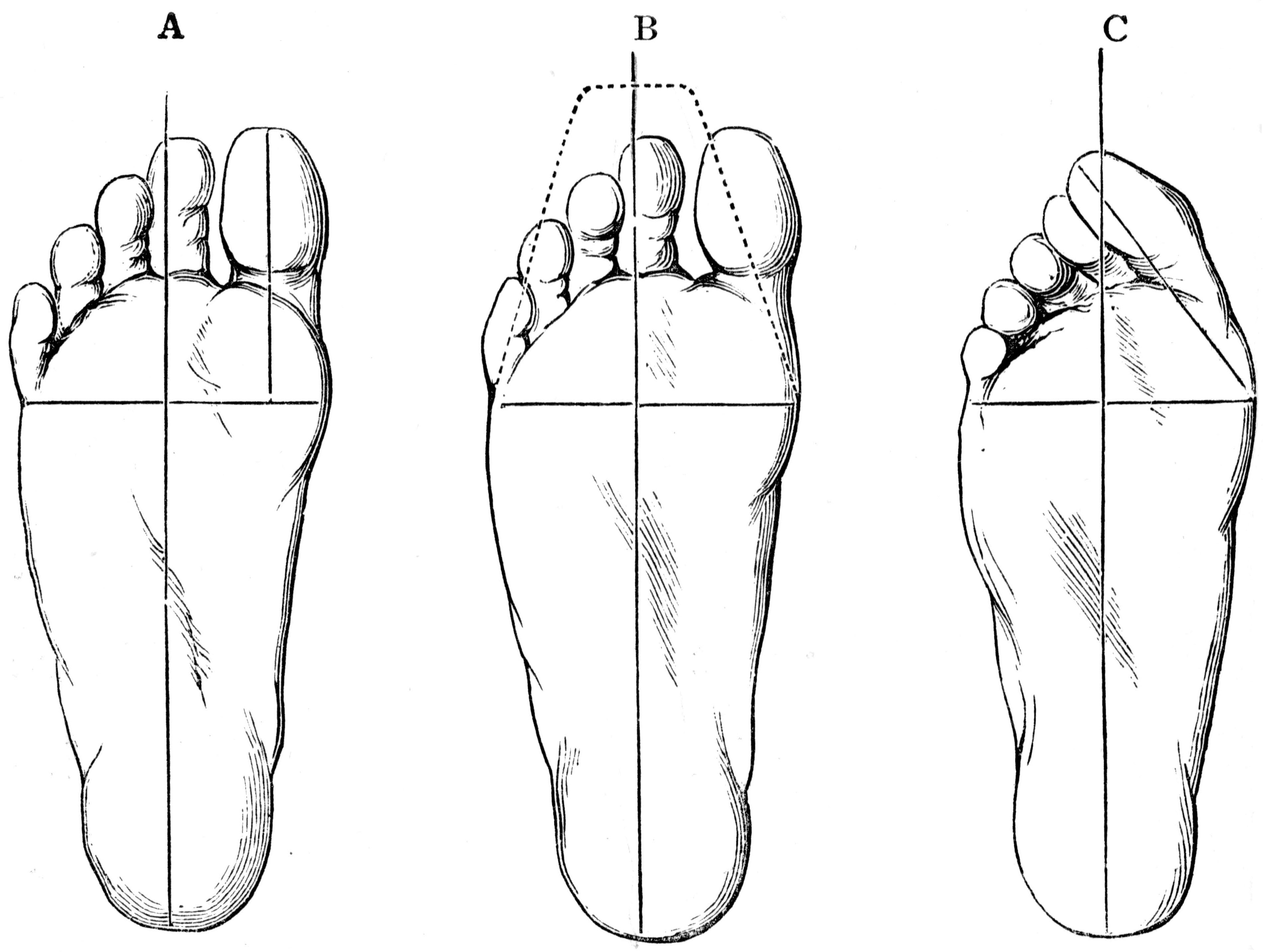 Symptoms
Symptoms Prevention
Prevention Overview
Overview


